
By Peter Wagner and Bernadette Rabuy
Wait, does the United States have 1.4 million or more than 2 million people in prison? Are most people in state and federal prisons locked up for drug offenses? Frustrating questions like these abound because our systems of confinement are so fragmented and controlled by various entities. There is a lot of interesting and valuable research out there, but varying definitions make it hard — for both people new to criminal justice and for experienced policy wonks — to get the big picture.
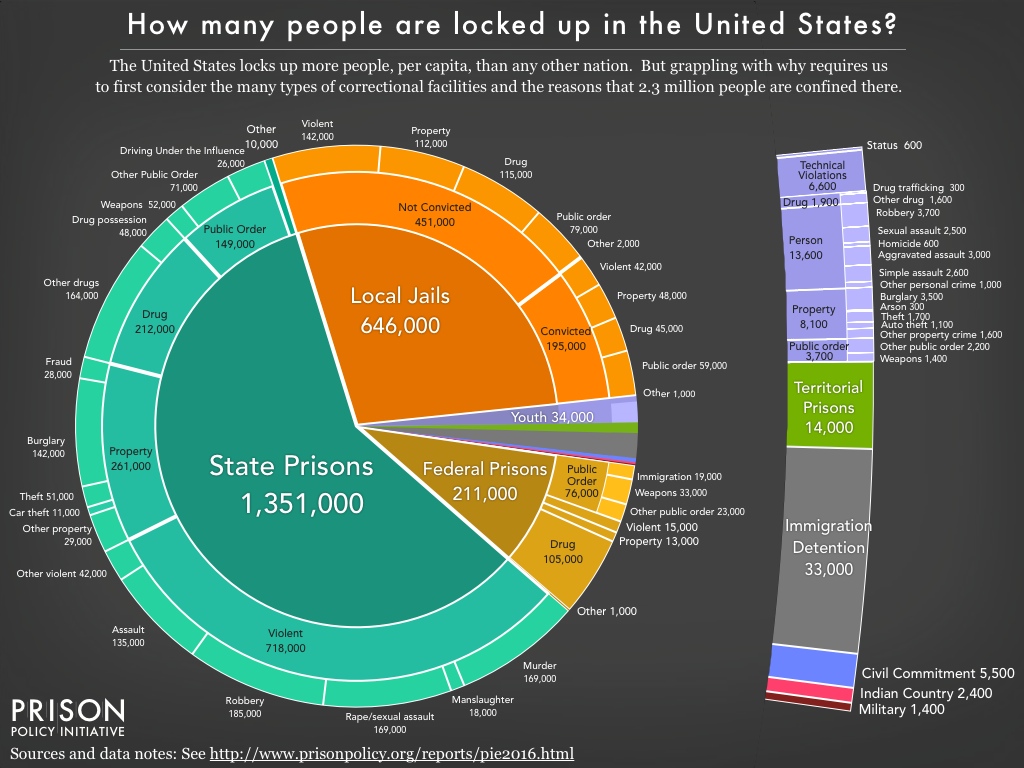
This report offers some much needed clarity by piecing together this country’s disparate systems of confinement. The American criminal justice system holds more than 2.3 million people in 1,719 state prisons, 102 federal prisons, 942 juvenile correctional facilities, 3,283 local jails, and 79 Indian Country jails as well as in military prisons, immigration detention facilities, civil commitment centers, and prisons in the U.S. territories. And we go deeper to provide further detail on why convicted and not convicted people are locked up in local jails.
While this pie chart provides a comprehensive snapshot of our correctional system, the graphic does not capture the enormous churn in and out of our correctional facilities and the far larger universe of people whose lives are affected by the criminal justice system. Every year, 636,000 people walk out of prison gates, but people go to jail over 11 million times each year. Jail churn is particularly high because most people in jails have not been convicted. Some have just been arrested and will make bail in the next few hours or days, and others are too poor to make bail and must remain behind bars until their trial. Only a small number (195,000) have been convicted, generally serving misdemeanors sentences under a year.
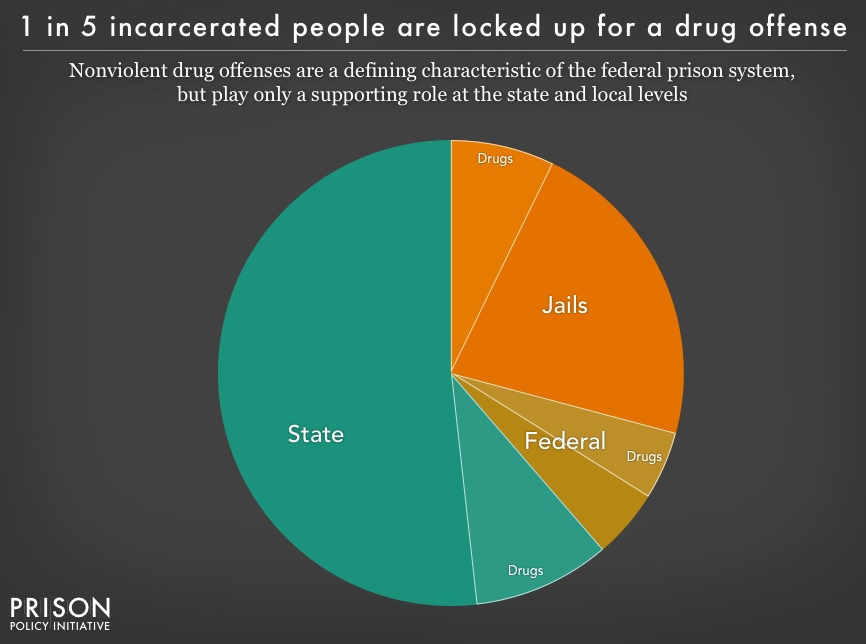
With a sense of the big picture, a common follow-up question might be: how many people are locked up for a drug offense? We know that almost half a million people are locked up because of a drug offense. The data confirms that nonviolent drug convictions are a defining characteristic of the federal prison system, but play only a supporting role at the state and local levels. While most people in state and local facilities are not locked up for drug offenses, most states’ continued practice of arresting people for drug possession destabilizes individual lives and communities. Drug arrests give residents of over-policed communities criminal records, which then reduce employment prospects and increase the likelihood of longer sentences for any future offenses.
All of the offense data presented comes with an important set of caveats. A person in prison for multiple offenses is reported only for the most serious offense so, for example, there are people in prison for “violent” offenses who might have also been convicted of a drug offense. Further, almost all convictions are the result of plea bargains, where people plead guilty to a lesser offense, perhaps of a different category or one that they may not have actually committed.
And many of these categories group together people convicted of a wide range of offenses. For example, “murder” is generally considered to be an extremely serious offense, but “murder” groups together the rare group of serial killers, with people who committed acts that are unlikely for reasons of circumstance or advanced age to ever happen again, with offenses that the average American may not consider to be murder at all. For example, the felony murder rule says that if someone dies during the commission of a felony, everyone involved is as guilty of murder as the person who pulled the trigger. Driving a getaway car during a bank robbery where someone was accidentally killed is indeed a serious offense, but few people would really consider that to be murder.
This “whole pie” methodology also exposes some disturbing facts about the youth entrapped in our juvenile justice system: Too many are there for a “most serious offense” that is not even a crime. For example, there are almost 7,000 youth behind bars for “technical violations” of the requirements of their probation, rather than for a new offense. Further, 600 youth are behind bars for “status” offenses, which are “behaviors that are not law violations for adults, such as running away, truancy, and incorrigibility.”
Turning finally to the people who are locked up criminally and civilly for immigration-related issues, we find that 19,000 people are in federal prison for criminal convictions of violating federal immigration laws. A separate 33,000 are civilly detained by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) separate from any criminal proceedings and are physically confined in special immigration detention facilities or in local jails under contract with ICE. (Notably, these categories do not include immigrants represented in other pie slices because of non-immigration related criminal convictions.)
Now, armed with the big picture of how many people are locked up in the United States, where, and why, we have a better foundation for the long overdue conversation about criminal justice reform. For example, the data makes it clear that ending the War on Drugs will not alone end mass incarceration, but that the federal government and some states have effectively reduced their incarcerated populations by turning to drug policy reform. Looking at the “whole pie” also opens up other conversations about where we should focus our energies:
- What is the role of the federal government in ending mass incarceration? The federal prison system is just a small slice of the total pie, but the federal government can certainly use its financial and ideological power to incentivize and illuminate better paths forward. At the same time, how can elected sheriffs, district attorneys, and judges slow the flow of people into the criminal justice system?
- Are state officials and prosecutors willing to rethink both the War on Drugs and the reflexive policies that have served to increase both the odds of incarceration and length of stay for “violent” offenses?
- Do policymakers and the public have the focus to confront the second largest slice of the pie: the thousands of locally administered jails? And does it even make sense to arrest millions of poor people each year for minor offenses, make them post cash bail, and then lock them up when they can’t afford to pay it? Will our leaders be brave enough to redirect corrections spending to smarter investments like community-based drug treatment and job training?
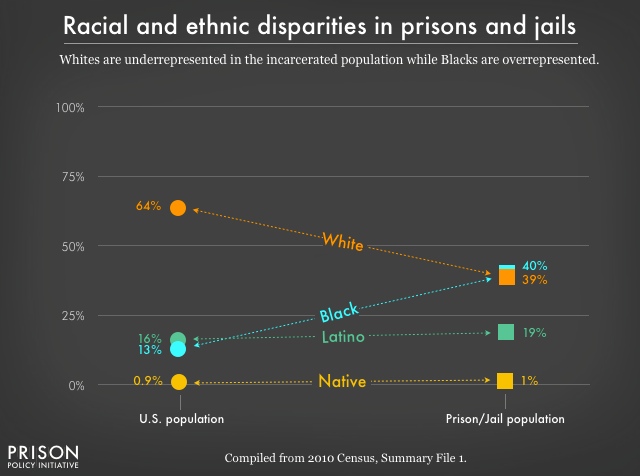
- Can we implement reforms that both reduce the number of people incarcerated in the U.S. and the well-known racial and ethnic disparities in the criminal justice system?
And once we have wrapped our minds around the “whole pie” of mass incarceration, we should zoom out and note that being locked up is just one piece of the larger pie of correctional control. There are another 820,000 people on parole (a type of conditional release from prison) and a staggering 3.8 million people on probation (what is typically an alternative sentence). Particularly given the often onerous conditions of probation, policymakers should be cautious of “alternatives to incarceration” that sometimes widen the net of criminalization to people who are not a threat to public safety.
Now that we can see the big picture of how many people are locked up in the United States in the various types of facilities, we can see that something needs to change. Looking at the big picture requires us to ask if it really makes sense to lock up 2.3 million people on any given day, giving this nation the dubious distinction of having the highest incarceration rate in the world. Both policymakers and the public have the responsibility to carefully consider each individual slice in turn to ask whether legitimate social goals are served by putting each category behind bars, and whether any benefit really outweighs the social and fiscal costs.
We’re optimistic that this “whole pie” approach can give Americans, who are ready for a fresh look at the criminal justice system, some of the tools they need to demand meaningful changes to how we do justice.
The data
This briefing uses the most recent data available on the number of people in various types of facilities and the most significant charge or conviction. Because not all types of data are collected each year, we sometimes had to, for example, apply the percentage distribution of offense types from the previous year to the current year’s total count data. For this reason, we choose to round all figures in the graphic to the nearest thousand, except for children, civil commitment, Indian Country jails and military prisons, which were rounded to the nearest hundred. This process may also result in some parts not adding up precisely to the total.
We used the most recent data available as of March 11, 2016 for:
- Jails: Bureau of Justice Statistics, Jail Inmates at Midyear 2014 page 1 and Table 2, reporting total population and convicted status for June 30, 2014 and our analysis of the Survey Of Inmates In Local Jails, 2002 for offense types. See below and Who is in jail? Deep dive for why we used our own analysis rather than the otherwise excellent Bureau of Justice Statistics analysis of the same dataset, Profiles of Jail Inmates, 2002.
- Immigration detention: William Selway and Margaret Newkirk, “Congress Mandates Private Jail Beds for 34,000 Immigrants”, Bloomberg News, September 24, 2013.
- Federal: Bureau of Justice Statistics, Prisoners in 2014, Table 1 and Table 12 reporting data as of September 30, 2014 (offense types) and December 31, 2014 (total population).
- State Prisons: Prisoners in 2014, Table 1 and Appendix Table 4 from data as of December 31, 2013 (offense types) and December 31, 2014 (total population).
- Military: Prisoners in 2014, Table 13 reporting data as of December 31, 2014.
- Territorial Prisons Correctional facilities in U.S. Territories (American Samoa, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands) and U.S. Commonwealths (Northern Mariana Islands and Puerto Rico): Correctional Populations in the United States, 2014 Appendix Table 4, reporting data for December 31, 2014.
- Youth: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, Easy Access to the Census of Juveniles in Residential Placement, reporting data for October 30, 2013. To keep things comparable with the other parts of the pie, we choose to include only those youth detained in detention centers, long-term secure facilities, and reception/diagnostic centers. Other placements outside the home are not included in Mass Incarceration: The Whole Pie 2016. Our data on youth incarcerated in adult facilities comes from the OJJDP’s Statistical Briefing Book sections on youth 17 and younger in adult prisons and jails. For more information on the geography of the juvenile system, see the Youth First Initiative.
- Civil Commitment (At least 16 states and the federal government operate facilities for the purposes of detaining people convicted of sexual crimes after their sentences are complete. These facilities and the confinement there are technically civil, but in reality are quite like prisons. They are often run by state prison systems, are often located on prison grounds, and most importantly, the people confined there are not allowed to leave.): Deidre D’Orazio, Ph.D., Sex Offender Civil Commitment Programs Network Annual Survey of Sex Offender Civil Commitment Programs, 2014.
- Indian Country (correctional facilities operated by tribal authorities or the U.S. Department of the Interior’s Bureau of Indian Affairs): Bureau of Justice Statistics Correctional Populations in the United States, 2014 Appendix Table 4, reporting data for June 30, 2014.
- Probation and Parole: Our counts of the number of people on probation and parole are from Correctional Populations in the United States, 2014, Table 1, Table 6 and Appendix Table 1, reporting data for December 31, 2014, and were adjusted to ensure that people with multiple statuses were counted only once in their most restrictive category. For readers interested in knowing the total number of people on parole and probation, ignoring any double-counting with other forms of correctional control, there are 856,900 people on parole and 3,864,100 people on probation.
Several data definitions and clarifications may be helpful to researchers reusing this data in new ways:
- To avoid anyone in immigration detention being counted twice, we removed the 16,384 people — cited in Table 8 of Jail Inmates at Midyear 2014 — confined in local jails under contract with ICE from the total jail population and from the numbers we calculated for those in local jails that are not convicted.
- To avoid anyone in local jails on behalf of state or federal prison authorities from being counted twice, we removed the 81,738 people — cited in Table 9 of Prisoners in 2014 — confined in local jails on behalf of federal or state prison systems from the total jail population and from the numbers we calculated for those in local jails that are convicted.
- Because we removed ICE detainees and people under the jurisdiction of federal and state authorities from the jail population, we had to recalculate the offense distribution reported in Profile of Jail Inmates, 2002 who were “convicted” or “not convicted” without the people who reported that they were being held on behalf of other agencies. Our definition of “convicted” was those who reported that they were “To serve a sentence in this jail,” “To await sentencing for an offense,” or “To await transfer to serve a sentence somewhere else”. Our definition of not convicted was “To stand trial for an offense,” “To await arraignment,” or “To await a hearing for revocation of probation/parole or community release”.
Acknowledgments
This 2016 report was made possible by a generous grant from the Public Welfare Foundation and the contributions of individuals across the country who support justice reform. The infographic slideshows and the graph of correctional control were made possible by Gabe Isman of our Young Professionals Network. Bob Machuga and J. Andrew World helped with design issues, and Alison Walsh helped us gather research. Melissa Sickmund at the National Center for Juvenile Justice and Todd Minton at the Bureau of Justice Statistics expanded our knowledge of agencies’ datasets; and Alex Friedmann, Neelum Arya and Drew Kukorowski provided invaluable feedback on earlier drafts of this report. Any errors or omissions, and final responsibility for all of the many value judgements required to produce a data visualization like this, however, are the sole responsibility of the authors.
Footnotes
- The number of state and federal facilities is from Census of State and Federal Correctional Facilities, 2005, the number of youth facilities is from Juvenile Residential Facility Census, 2012: Selected Findings (we included only detention centers, reception/diagnostic centers, and training schools/long-term secure facilities but not shelters, group homes, ranch/wilderness camps, and residential treatment centers), the number of jails from Census of Jail Facilities, 2006 and the number of Indian Country jails from Jails in Indian Country, 2014. We aren’t currently aware of a good source of data on the number of the facilities of the other types. ↩
- Eleven million jail admissions probably amounts to less than 11 million unique individuals cycling through jails in a year. According to a presentation, The Importance of Successful Reentry to Jail Population Growth [Powerpoint] given at The Jail Reentry Roundtable, Bureau of Justice Statistics statistician Allen Beck estimates that of the 12-12.6 million jail admissions in 2004-2005, 9 million were unique individuals. ↩
- The local jail population in the pie chart excludes the people being held in jails for other agencies so the population physically in jails (744,592) is larger than the population under jail jurisdiction reflected in the pie chart (646,000). See Table 1 of Jail Inmates at Midyear 2014. The “not convicted” population is driving jail growth. ↩
- The data doesn’t show how many people are convicted of drug law violations and are held in territorial prisons or Indian Country jails. The military prison system holds less than 100 people for drug law violations. ↩
- In 2012, there were 1,552,432 drug arrests in the U.S., the far majority of which were for drug possession or use rather than for sale or manufacturing. See Arrest Data Analysis Tool. ↩
- The federal government defines the hierarchy of offenses with felonies higher than misdemeanors. And “[w]ithin these levels, … the hierarchy from most to least serious is as follows: homicide, rape/other sexual assault, robbery, aggravated assault, burglary, larceny/ motor vehicle theft, fraud, drug trafficking, drug possession, weapons offense, driving under the influence, other public-order, and other.” See page 13 Recidivism of Prisoners Released in 1994. ↩
- The felony murder rule has also been applied when the person who died was a participant in the crime. For example, if one of the bank robbers is killed by the police during a chase, the surviving bank robbers can be convicted of felony murder of their colleague. For example see People v. Hudson, 222 Ill. 2d 392 (Ill. 2006) and People v. Klebanowski, 221 Ill. 2d 538 (Ill. 2006) ↩
- In 2013, more than half of juvenile status offense cases were for truancy. See page 66 of Juvenile Court Statistics 2013. ↩
- Our report on the pre-incarceration incomes of those imprisoned in state prisons, Prisons of Poverty: Uncovering the pre-incarceration incomes of the imprisoned, found that, in 2014 dollars, incarcerated people had a median annual income that is 41% less than non-incarcerated people of similar ages. Our preliminary analysis of jail data shows that people in jails may have even lower incomes. For pre-incarceration incomes of those in jails in 2002, see page 9 of Profile of Jail Inmates, 2002. ↩
- Recall from above that people go to jail over 11 million times each year. ↩
- This is the most recent data available until the Bureau of Justice Statistics begins administering the next Survey of Inmates in Local Jails in 2018. ↩
- Notably, the number of people admitted to immigration detention in a year is much higher than the population detained on a particular day. The immigration detention system took in 440,600 people during the course of 2013. See page 1 of Immigration Detention: Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen Management and Oversight of Facility Costs and Standards. ↩
- Responses to whether someone reported being held for an authority besides a local jail can be found in V113, or V115-V118 in the Survey of Inmates in Local Jails, 2002 Codebook. ↩



Be the first to comment